Now Reading: 160-million-year-old blue-stain fungi in China found to be harmful to trees |
-
01
160-million-year-old blue-stain fungi in China found to be harmful to trees |
160-million-year-old blue-stain fungi in China found to be harmful to trees |

In a groundbreaking discovery, researchers have uncovered 160-million-year-old blue-stain fungi fossils from the Jurassic Tiaojishan Formation in China. The new findings supply recent insights into the ecological relationships between blue-stain fungi, crops, and bugs throughout the Jurassic interval. These fungi are typically nonfatal to their hosts however usually speed up tree mortality when related to wood-boring bugs.According to ScienceDaily, a Chinese workforce of scientists highlights the invention of well-preserved blue-stain fungal hyphae inside Jurassic fossil wooden from northeastern China, pushing again the earliest recognized fossil document of this fungal group by roughly 80 million years.
Know in regards to the blue-stain fungi, lethal to trees
Blue-stain fungi are recognized for his or her capability to colonize wooden, significantly in conifer trees, inflicting attribute discoloration in the sapwood. While these fungi don’t decompose wooden, they usually trigger appreciable harm when related to wood-boring bugs. Their function in accelerating tree mortality is critical, but their evolutionary origins have lengthy remained a thriller. Molecular phylogenetic analyses counsel that blue-stain fungi are an historic fungal group, presumably originating throughout the Late Paleozoic or early Mesozoic.This latest discovery in China revises our understanding of blue-stain fungi’s historical past, suggesting their origins hint a lot additional again into Earth’s previous.Dr. Ning Tian, a paleontologist at Shenyang Normal University, defined the rarity of such findings: “Not until 2022 was the first credible fossil record of blue-stain fungi reported from the Cretaceous in South Africa, with an age of approximately 80 million years.”
Discovery of the fossils of the blue-stain fungus
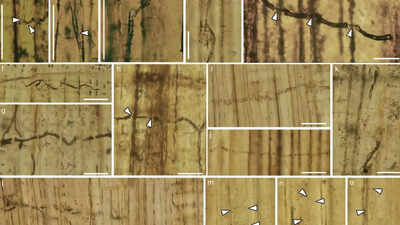
The fossils have been found contained in the petrified wooden of Xenoxylon phyllocladoides, a kind of conifer tree from the Jurassic interval in western Liaoning province, China. Researchers found dark-colored fungal threads referred to as hyphae, that are typical of blue-stain fungi. “Under the microscope, the fossil hyphae appear dark, showing pigmentation that is a key feature of modern blue-stain fungi, which cause wood to change color,” the workforce defined. This exhibits that these fungi have existed for thousands and thousands of years and are related to fungi we see right now.The researchers additionally found a particular construction the fungi use to enter the wooden. “When the fungi penetrate the wood’s cell walls, the hyphae often form a structure called a penetration peg,” they stated. This peg helps the fungi break by the robust wooden cells by mechanical power, which is totally different from different fungi that use enzymes to break down wooden.
A serious leap in the fossil document of blue-stain fungi
The discovery of the blue-stain fungi found in China not solely fills a spot in the fossil document but in addition supplies important proof for understanding the early evolution of blue-stain fungi and their ecological interactions. The proven fact that these fungi have been already established in the Jurassic interval means that their relationship with wood-boring bugs, that are possible the primary brokers for spore dispersal, was already in place lengthy earlier than the arrival of recent insect speciesThe fossilized blue-stain fungi signify a major milestone in paleontological analysis. “The finding of Jurassic blue-stain fungi from China represents the second report of the blue-stain fungi and the earliest fossil record of this fungal group in the world, pushing back the earliest known fossil record of this fungal group by approximately 80 million years,” stated Dr. Yongdong Wang, a paleontologist on the Nanjing Institute of Geology and Paleontology.