Now Reading: Astronomers capture rare images of infant planet WISPIT 2b in multi-ringed birth disk |
-
01
Astronomers capture rare images of infant planet WISPIT 2b in multi-ringed birth disk |
Astronomers capture rare images of infant planet WISPIT 2b in multi-ringed birth disk |
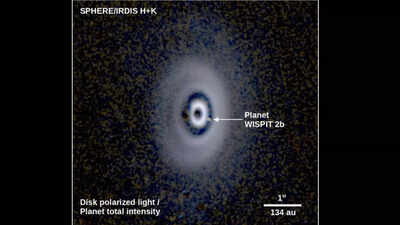
Astronomers have made a groundbreaking discovery that would change how we perceive the birth of planets. Using the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope (VLT) in Chile, researchers have discovered a younger planet, named WISPIT 2b, orbiting a star round 430 gentle years away. What makes this so particular is that the planet sits inside a multi-ringed protoplanetary disk – a dusty, gas-filled construction the place planets kind. This is the primary confirmed detection of its sort, and it affords scientists a rare glimpse into how planetary methods, together with our personal photo voltaic system, might have developed billions of years in the past. The group’s analysis was printed throughout two papers in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
About the younger planet 5 occasions greater than Jupiter: WISPIT 2b
WISPIT 2b is a fuel big planet, regarded as concerning the dimension of Jupiter however a lot youthful – solely 5 million years previous. In cosmic phrases, that makes it an infant in comparison with Earth’s photo voltaic system, which is round 4.6 billion years previous. Despite its youth, WISPIT 2b is already large, estimated to be as much as 5 occasions greater than Jupiter. Because it’s nonetheless forming, the planet glows faintly from the warmth of its creation, making it seen in infrared gentle.
How astronomers captured the primary images of WISPIT 2b’s multi-ringed disk
Researchers used the Very Large Telescope (VLT) in the Atacama Desert of Chile to capture images of WISPIT 2b. At first, they had been solely conducting quick “snapshot” observations of many younger stars, hoping to identify planets. Instead, they observed a ravishing multi-ringed disk round WISPIT 2. Follow-up observations confirmed the glowing presence of WISPIT 2b inside one of the disk’s gaps. Later, astronomers from the University of Arizona captured images in seen gentle, proving that the planet remains to be actively gathering materials.
WISPIT 2b discovery reveals how younger planets form their environment
WISPIT 2b was found inside a multi-ringed protoplanetary disk – a construction of fuel and mud that orbits younger stars and serves because the birthplace of planets. While astronomers have noticed a whole lot of such disks, recognizing a planet clearly inside one is extraordinarily rare. WISPIT 2b is the primary confirmed planet inside a disk with a number of gaps and rings, making it a singular alternative to check how planets form and work together with their environment.This discovery can also make clear how our personal photo voltaic system shaped 4.5 billion years in the past. The disk round WISPIT 2 spans about 380 occasions the Earth–Sun distance, with WISPIT 2b carving seen channels by the mud. These options present scientists with helpful clues about how younger planets clear paths in their birth environments, just like the early processes that formed Earth, Jupiter, and the opposite planets in our photo voltaic system.
What is a protoplanetary disk
A protoplanetary disk is sort of a cosmic nursery. It kinds when fuel and mud left over from star formation collect into an enormous, spinning disk. Inside this disk, clumps of materials stick collectively, rising into planets. Many disks present gaps and rings, which recommend planets are forming and pulling materials in direction of themselves. Until just lately, most of this was idea. Now, with WISPIT 2b, scientists have direct proof of a younger planet at work inside such a disk.
Exoplanets defined: What makes WISPIT 2b so particular
Exoplanets are planets that orbit stars outdoors our photo voltaic system. More than 5,800 exoplanets have been found thus far, and astronomers consider billions extra exist in our galaxy alone. Some exoplanets are rocky like Earth, whereas others are big fuel worlds like Jupiter. WISPIT 2b is very helpful as a result of it reveals us what planets appear to be in their earliest levels of progress, one thing hardly ever noticed till now.
A rare benchmark system: What WISPIT 2b reveals about planets
Astronomers name this technique a “benchmark” for planet formation research. WISPIT 2 is just like our Sun however a lot youthful, making it an ideal check case to check with how Earth’s photo voltaic system developed. Capturing direct images of such younger planets is extremely difficult, which is why scientists are thrilled. According to the analysis group, this discovery will information future research and will even clarify why different planetary methods look so completely different from our personal.Also learn | 10 fascinating information concerning the Milky Way galaxy









