Now Reading: NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope discovers earliest galaxy ever seen in the universe |
-
01
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope discovers earliest galaxy ever seen in the universe |
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope discovers earliest galaxy ever seen in the universe |
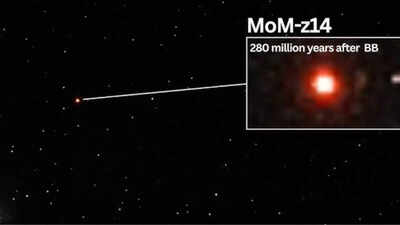
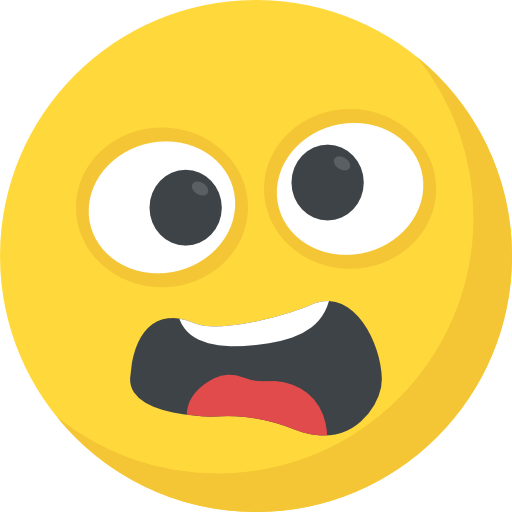
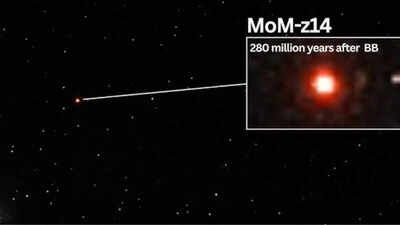
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has as soon as once more made historical past by discovering the most distant and historical galaxy ever noticed, named MoM z14. Located simply 280 million years after the Big Bang, this galaxy pushes the boundaries of cosmic statement. The discovering highlights JWST’s distinctive capability to look into the early universe, providing unprecedented insights into the formation of the first galaxies. With its record-breaking redshift of z = 14.44, MoM z14 not solely redefines our understanding of galaxy evolution but in addition means that even earlier galaxies could quickly be inside attain, marking a brand new period in astronomy.
JWST discovers one in all the earliest galaxies shaped after the Big Bang
NASA’s $10 billion area telescope has noticed a galaxy that was current solely 280 million years after the Big Bang, a time that astronomers discuss with as “cosmic dawn.” The discovery crew dubbed this galaxy MoM z14—”Mother of all early galaxies” for brief.“First and foremost, at the moment, this is the most distant object known to humanity,” mentioned Pieter van Dokkum, Yale University professor of Astronomy and Physics, in an interview. “MoM z14 existed when the universe was about 280 million years old—we’re getting quite close to the Big Bang. Just to put that in context, sharks have been around on Earth for a longer timespan!”Since getting into service in mid-2022, the JWST has been excellent at detecting very distant galaxies via an impact referred to as redshift. When the universe will get greater, gentle from previous galaxies will get stretched, transferring towards the crimson finish of the spectrum. The extra distant and thus older the galaxy is, the increased the redshift. Prior to MoM z14, the then-record holder was a galaxy named JADES-GS-z14-0, seen at a redshift of z = 14.32, some 300 million years following the Big Bang. MoM z14 is all the extra spectacular with a redshift of z = 14.44, extending fashionable astronomy’s observational limits.
Discovery of MoM z14 reshapes the view of galaxy formation
In van Dokkum’s view, the discovery of MoM z14 just isn’t merely a brand new report—it provokes earlier hypotheses on the early formation of galaxies. “The bigger picture here is that JWST wasn’t supposed to discover any galaxies this early in the universe’s history at least, or at least at this point in the mission,” he states.Previous JWST fashions predicted considerably fewer vivid galaxies in the universe’s early days. Current observations point out greater than 100 such galaxies exist in the early universe—considerably greater than earlier than.
What units MoM z14 aside
Aside from its record-setting age, scientists have been in a position to glean helpful perception into MoM z14’s composition and construction:
- Size: Roughly 50 occasions smaller than the Milky Way.
- Star formation: The galaxy possesses unexplained emission traces displaying that this can be very younger and shortly producing new stars.
- Chemical composition: Existence of carbon and nitrogen, which suggests that it isn’t one in all the absolute first technology galaxies.
“These things suggest that there had to be previous galaxies made only of hydrogen and helium that existed prior to MoM z14,” mentioned van Dokkum. “MoM z14 might be the first generation of ‘normal’ galaxies that started making heavier elements using processes in stars.”Also Read | Meteorite that hit Earth 3.26 billion years in the past could have sparked excellent news for all times, research reveals